Jagadish Chandra Bose | Inventions, Education, & Biography
Learn about the life and achievements of Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose, the Indian scientist, polymath, and visionary. About their inventions, education, biography, From pioneering research on radio waves to demonstrating plant sensitivity.

Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose (1858–1937) was a visionary Indian scientist, polymath, and pioneer in various fields, including biology, physics, and botany. His groundbreaking work across multiple disciplines left an indelible mark on the scientific community. Let’s explore the life and achievements of this extraordinary figure.
Quick Information
- Birth: November 30, 1858, in Mymensingh, Bengal, India (now Bangladesh).
- Death: November 23, 1937, in Giridih, Bihar, India (aged 78).
Subjects of Study
- Stimulus-Response Behavior: Bose demonstrated that plants, like animals, respond to various stimuli such as heat, cold, light, and sound, showing remarkable sensitivity to their environment.
Scientific Contributions
- Radio Waves and Coherer:
- Bose’s 1895 experiments on the properties of short radio waves led to significant advancements in the coherer, a radio wave detector. His work laid the foundation for solid-state physics.
- Plant Physiology:
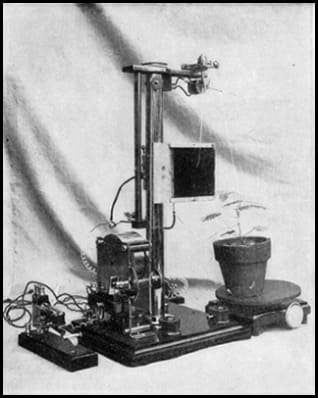
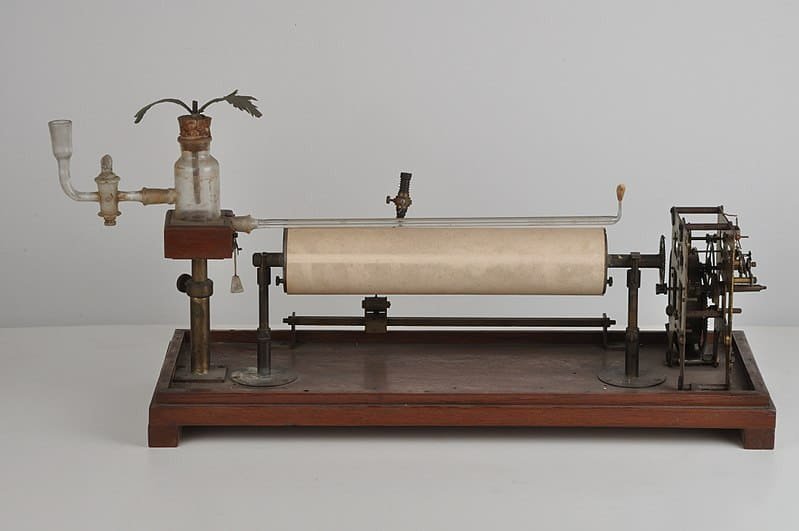
- Invented the crescograph, a device that precisely measures plant growth.
- Proved that plants exhibit responses to external stimuli, including a noticeable reaction when injured, akin to a "feeling" mechanism.
- Bose Institute:
- Established the Bose Institute in Kolkata in 1917, the first interdisciplinary research center in Asia, where he served as Director until his death.
Early Life and Education
Born on November 30, 1858, in Bikrampur, Bengal Presidency (now in Bangladesh), Bose began his education at Dhaka Collegiate School. He later studied at St. Xavier's College, Calcutta and went on to the University of London, where he initially pursued medical studies before health issues forced him to switch to physics.
Pioneering Research
- Radio Waves and Coherer:
- Bose’s experiments with radio waves in the microwave spectrum led to enhancements in the coherer, influencing the development of radio technology and solid-state physics.
- Plant Physiology:
- Bose invented the crescograph to measure the growth of plants and demonstrated that plants react to stimuli, suggesting that they have a type of "feeling."
- His work, including the book Response in the Living and Non-Living (1902), explored these ideas.

Legacy and Honors
- Regarded as the father of Bengali science fiction, Bose skillfully merged scientific principles with creative storytelling.
- A crater on the Moon is named in his honor, commemorating his vast contributions to science.
- He established the Bose Institute, which continues to foster cutting-edge research.
Conclusion
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose's contributions go beyond scientific advancements. His relentless curiosity and passion for knowledge continue to inspire scientists and thinkers across the globe. His legacy, encapsulated in his work on radio waves, plant physiology, and the Bose Institute, remains a guiding light for future generations.

 Deepak Maurya
Deepak Maurya 





























